Published on
What is a Content Delivery Network? (CDN)

As the demand for media-rich content grows, so do the performance expectations of consumers. One of the greatest challenges online businesses face is to deliver large amounts of content to audiences spread out across the globe as quickly as possible.
The solution is a content delivery network (CDN).
CDNs Explained
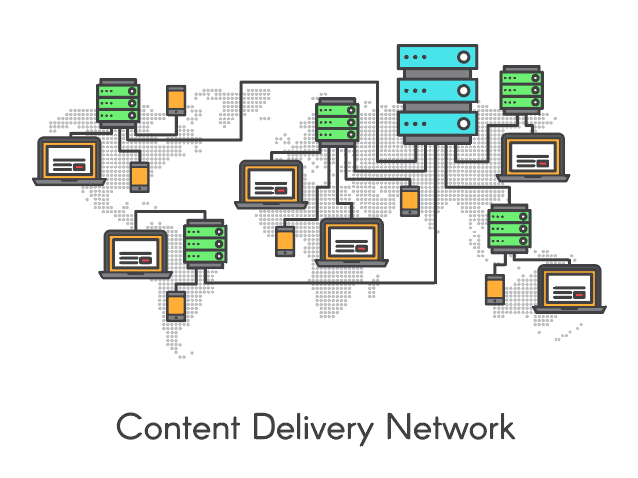
A CDN is a geographically distributed network of servers designed to increase website loading times regardless of where end users are located. Often referred to as an edge server, CDNs ensure queries are routed to the resource closest to where the end user resides. Since the physical distance between your content and your users is shortened, the time it takes for content to appear on a user’s screen is significantly decreased or eliminated altogether.
How Do CDNs Work?
The reason CDNs are able to enhance the speed of your website is because it improves latency. This is possible through content caching servers located at strategically positioned points of presence (PoPs) around the world. Since the physical gap between servers and end users is closed, data has less distance to travel. Think of it in terms of GPS. There are many different ways to get to a destination, but unless you’re sightseeing, you want the fastest route. That’s where a CDN comes in. Much like GPS, which chooses the fastest driving route by default, when using a CDN, requests are always sent via the fastest option, or more specifically, the closest location to the requester.
Who Uses CDNs?
Any brand that offers dynamic content to a large and/or global audience can benefit from a CDN. Most major brands use multiple CDNs for optimal end-user experiences. Examples of dynamic content include e-commerce sites, social media platforms, gaming sites, video sites, or any other website or application with media-rich content and multiple users.
CDN Benefits
Here are some quick facts as to why CDNs are beneficial to domain owners:
- Scalable
- Faster page load times
- Enhanced performance
- Improved stability
- Audience segmentation
- Decreased server load
- Packet loss reduction
- Bandwidth reduction
Cons of CDNs
Like anything else, content delivery networks do have some downsides:
- High costs for large volumes of traffic
- Outages and performance degradation
- Support
- Location gaps
Tip: Using Multi-CDN can eliminate the risk of outages, performance degradation, and fill in any location gaps.
Recommended CDNs
We frequently analyze content delivery network speed and performance. Here are some of our top recommendations for high-performing CDNs:
- Limelight
- ArvanCloud
- CacheFly
- EDJX
- G-Core
- Melbicom (SwiftyCDN)
- 5centsCDN
- Nusec
- Blazing CDN
- BunnyCDN
- Globo CDN
CDNs in a Nutshell
Overall, the benefits of a CDN, especially when using more than one, far outweighs the cons. CDNs will reduce latency, greatly improve load times, and provide an overall performance boost for your site by delivering content based on the geographical location of your end users.
Related Resources: